Blog

Why Your Actions Matter?
Every year, two powerful environmental awareness events remind us why our choices matter—National Renewable Energy Day, observed on March 21st, and Earth Hour, held annually on the last Saturday of March. While the dates stay the same, the message behind them remains urgent and timeless: our planet needs action now.
These events aren’t just symbolic—they’re a global wake-up call. The good news? Even small actions can lead to significant, positive change. Here’s why these observances matter all year long—and how you can take part anytime.
Why dedicate a whole day to renewable energy? Because the world is still heavily dependent on fossil fuels, and that dependence comes with a steep environmental cost. Fossil fuels are not only finite—they’re also a leading contributor to climate change.
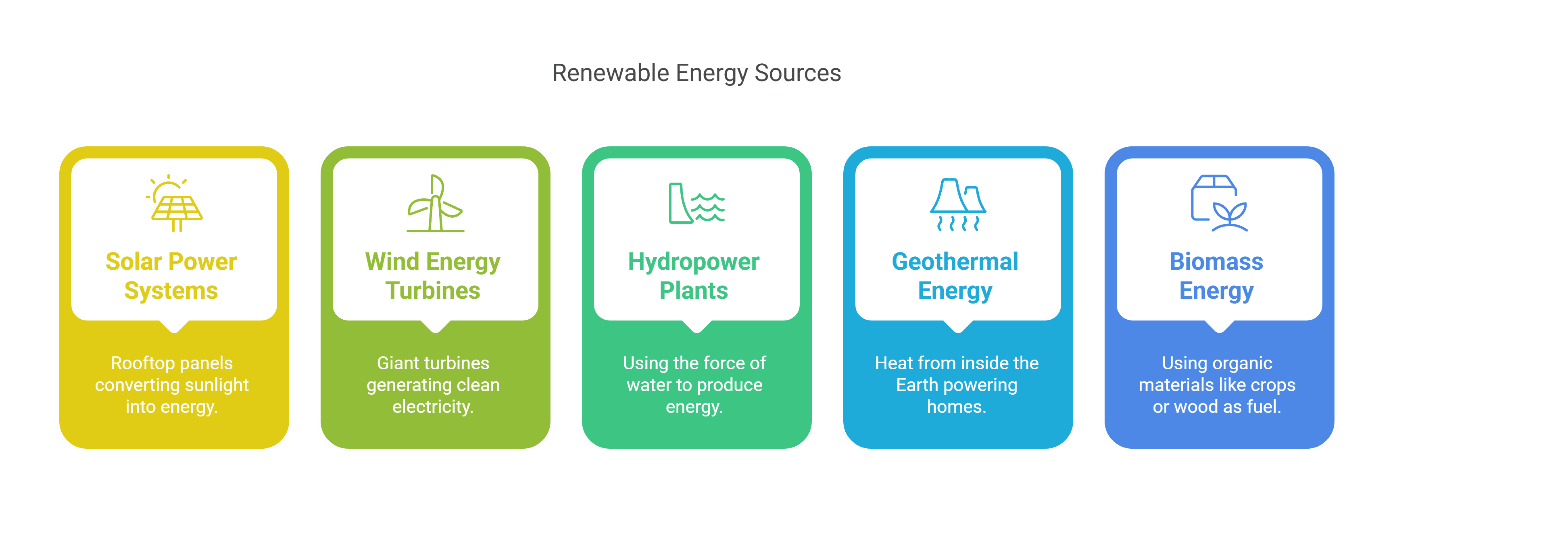
Since its start in 2004, National Renewable Energy Day has promoted clean, sustainable energy sources such as:
Today, renewable energy isn’t just a futuristic idea—it’s a growing reality. Countries worldwide are increasing their investments, and renewable energy capacity is expected to more than double by 2030.
Earth Hour, initiated in 2007 by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), began as a symbolic hour of darkness to raise awareness about climate change. It happens every year on the last Saturday of March at 8:30 p.m. local time, but its message resonates every day.
The current theme, “Give an Hour for Earth,” expands the concept beyond just turning off lights. It’s about giving one hour of your time to the planet by:
🌍 Learning about sustainable living
🌍 Volunteering in your community
🌍 Cleaning up a local park
🌍 Planting trees
🌍 Committing to a lower-carbon lifestyle
Even outside of that specific hour, Earth Hour encourages a simple truth: individual actions matter.
While National Renewable Energy Day promotes long-term change through clean energy and sustainable innovation, Earth Hour focuses on the power of individual effort and everyday choices.
Together, they represent a unified movement toward a healthier planet. National Renewable Energy Day lays the foundation for a fossil-fuel-free future, and Earth Hour energizes individuals to be part of the solution—starting now.
Ready to get involved? You don’t need a special occasion to take action. Here are some practical steps you can take today:
The shift is happening. More nations are investing in renewable infrastructure. More companies are prioritizing sustainability. And more individuals—like you—are making conscious choices to reduce their impact.
At LA Solar Group, we’re committed to making renewable energy accessible, affordable, and effective for homes and businesses. Whether you’re considering solar panels or simply cutting back on energy usage, every step matters.
So, whether it’s March 21st, Earth Hour, or any day of the year, your actions truly make a difference.
The Role of Solar Energy in Achieving Earth Day 2025 Goals
Understanding Your Electric Bill After Going Solar
MAKE THE SWITCH TO SOLAR ENERGY
- Research solar panel options for your home. (They can reduce your utility bills!)
- Look into community solar, wind, or hydropower programs in your area.
Participate in Earth Hour
- Turn off non-essential lights for one hour
- Use that hour to plan eco-friendly habits
- Host a local event or share tips online
Cut Down Your Energy Use
- Replace old bulbs with energy-efficient LEDs
- Unplug devices when not in use
- Invest in energy-saving appliances
Speak Up and Take Action
- Share educational content on social media
- Encourage local leaders to support sustainable policies
- Support green energy businesses in your area

